Smart Factory + Industry 4.0: How Microsoft technology is bringing major changes to manufacturing
Smart Factories are a key example of the thundering changes of Industry 4.0, where people, machines, resources and products are intelligently connected to fuel the exchange of information in real-time and with previously unimagined efficiency.
With Smart Factories, all components within an interconnected manufacturing plant work automatically towards predefined goals and take the most productive and efficient routes possible with multiple software solutions including automation and IoT. In the Smart Factory, people are no longer actively involved in the production process, but control and monitor production steps using intelligent reports and software dashboards.
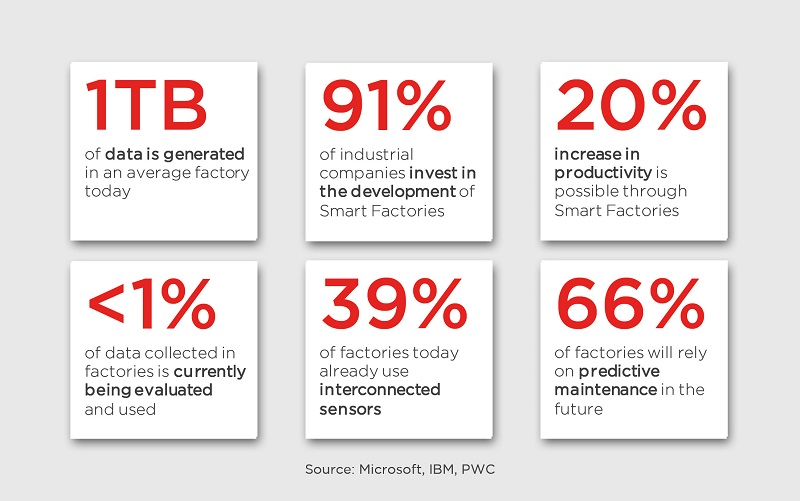
Facts and figure
Characteristics
All components in the manufacturing process communicate wirelessly with each other (e.g. RFID, Bluetooth) while, networked, intelligent cloud services operate to ensure flexibility. Cognitive technologies combine sensor-based information with machine learning, AI and IoT. Big Data technologies capture data and make it actionable, while predictive maintenance enables proactive servicing of machines and systems. On the other hand, embedded systems ensure monitoring of the Smart Factory and fast intervention in production processes by employees. When it comes to manufacturing processes and the Smart Factory as a whole, digital twins of products enable simulations of the production process during the development phase.
Key technologies
- Networked sensors (today: 39%, in future: 64%)
- Predictive Maintenance (today: 28%, in the future: 66%)
- Digital twins (today: 19%, in the future: 44%)
- 3D printing (18% today, 37% in the future)
- Autonomous intra-plant logistics (17% today, 35% in the future)
- Virtual / Augmented Reality (today: 13%, in the future: 33%)
- Humanoid robots (today: 12%, in the future: 22%)
- Artificial intelligence (today: 9%, in the future: 20%)
- Drones (today: 2%, in the future: 4%)
Source: Digital Factories 2020 – Shaping the future of Manufacturing, pwc
Challenges
In most factories, the individual plants and components are still working completely isolated from each other. An example of one of the major consequences of this poor use of existing technology, all the data that accumulates ends up siloed, in other words in isolated systems. There is a great need for investment here – for example in a common platform, improved connectivity and better device security. The latter also in order to meet the high security standards of the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC).
Digitalization is not only making it possible to collect data, but is also making reliable processing, storing and distributing of data a priority in order to enable intelligent and automated reactions in real time. This is where most manufacturing companies must first invest in infrastructure (e.g. new systems, tools or interfaces).
No employees in the Smart Factory?
When it comes to highly automated and digitized Smart Factories, it seems reasonable to assume that humans are unnecessary in the manufacturing process. The reality, however, shows that this is not the case – it is still impossible to imagine production processes without people.
Human roles have only shifted. Managers use data from hyper-networked smart factories to develop tailor-made, meaningful products and services. Factory workers use real-time insights to predict and prevent machine failures and can work more efficiently and productively with mixed-reality devices, IoT-enabled machines and AI-enhanced applications.
Benefits of industry 4.0. technology for Smart Factory
- Lean processes
- High and consistent quality
- Savings in development and production costs
- Short development and production times
- Error and risk minimization
- Minimization of plant downtimes
- Maximizing production throughput
- Fast innovation cycles
- Fast and flexible adaptation of products and processes to market requirements
- Low personnel expenses
- Low warehousing costs
Microsoft makes Smart Factories possible
With Dynamics 365 and Azure IoT, Microsoft makes smart factories possible today. Well-known firms in the manufacturing industry such as Airbus, Rolls-Royce and Honewell, have already successfully converted their operations to this more innovative model. But you don’t have to be a multinational to benefit from Smart Factory technology. Discover how your organization can benefit from Smart Factories by contacting us today!




